EFFECT OF VARIOUS EXTRACTS FROM FICUS RETUSA L. STEM BARK ON WOUND HEALING POTENTIAL
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ijraps.v8i2.159Keywords:
Ficus retusa, Wound healing, Incision and Excision, Povidone iodine.Abstract
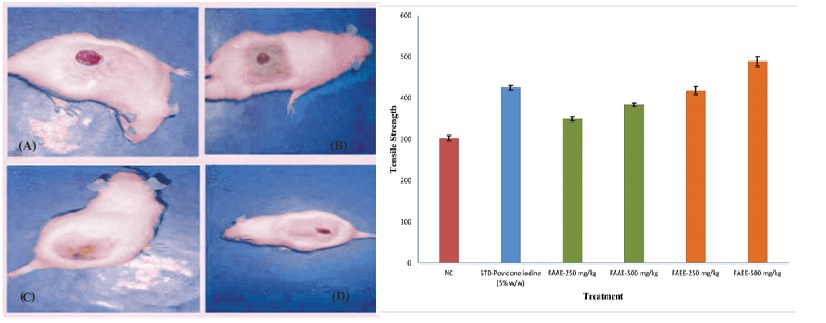
A wound is defined as a disruption in the physiological continuity and structural integrity of a living tissue. It can be caused by physical, chemical, thermal, microbiological, or immunological damage to the tissue. Plants have enormous potential for wound surveillance and care. In many nations, ancient and traditional medicine employs a wide range of herbs to heal wounds. These common agents promote healing and regeneration of the damaged tissue in a variety of ways. The acetone and ethanolic extracts of Ficus retusa stem bark have been taken to evaluate the wound healing potential in excision and incision wound models. The parameters studied include the rate of wound contraction, period of complete epithelialization of the excision model, and tensile strength of the incision wound. A one-way ANOVA test was used to analyze the results obtained from the present study and p<0.05 was considered significant. Both acetone and ethanolic extracts of F. retusa were found to possess significant wound-healing activity, which was evidenced by a decrease in the period of epithelialization, an increase in the rate of wound contraction, and skin-breaking strength. The present study has demonstrated that the acetone and ethanolic extracts of F. retusa have properties that render them capable of promoting accelerated wound-healing activity compared with standard drug and normal control.
Downloads