Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Deepika Rasa
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ijraps.v2i11.59Keywords:
Deepika rasa, Antibacterial study, BacteriaAbstract
Now a day’s infectious diseases are posing problem for human beings. In modern era for the development of Ayurvedic medicine with the proof scientifically and use of new search antibiotics to be increase, So we studied for pharmaceutical & diagnostic parameter standardization of Deepika rasa. Deepika rasa is not popular traditional medicine so an attempt has been made to develop a safe & less expensive antimicrobial drug.
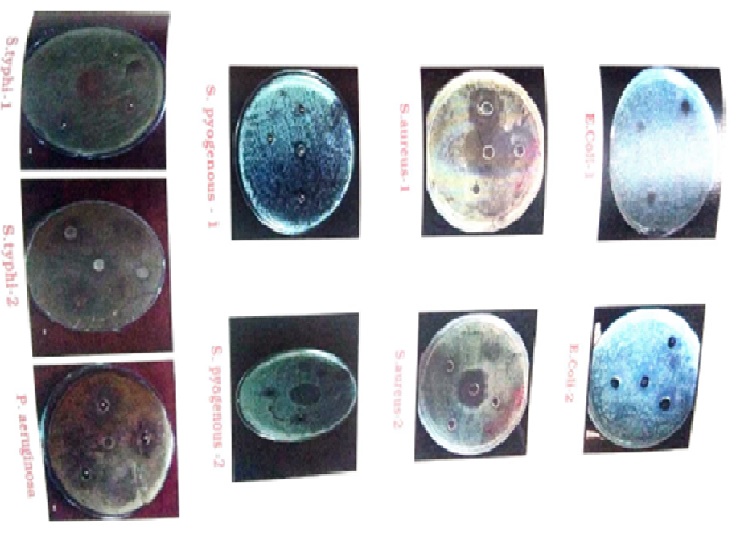
Deepika rasa formulations are selected for the present study from Rasa rattan samuccaya (U.K.A12). Deepika rasa was indicated as “Sarva Jwarhar Vinashanam”. The antibacterial activity of the Deepika rasa was tested against 5 pathogenic bacterial strain Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella typhi. These pathogens are very common for fever.
In order to study antibacterial action of Deepika rasa in vitro well diffusion method. During this study Deepika rasa was trailed with bacterial at different concentration. To correlate the result control solution were prepared by streptomycin. Experimental group were compared with control group and observation were noted.
The encouraging results obtained from anti microbial study of Deepika rasa. Deepika rasa was highly significant for some pathogen with the different concentration & moderately significant for some pathogen with the different concentration & no significant for some pathogen with the different concentration. So an attempt was made to find a safe and effective Ayurvedic medicine.
Downloads